The original document file format of the conversion source is docx file only. doc format files saved in old Microsoft Word are not subject to conversion processing.
By default, tags that conform to the HTML specifications are output.
◎ HTML specification reference
If you specify “-xhtml” parameter as a conversion option, XHTML 1.0 compliant tags will be output.
In addition, the tag samples of the following conversion specifications explain the state of conformance to the HTML specifications.
| Conversion source | Conversion destination (HTML tag) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Root | <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang=""> |
Japanese ver.: lang=”ja” English ver.: lang=”en” See Note 1 for language judgment. The language can also be specified by a parameter in the conversion options. |
| Character encoding | <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> | UTF-8 is the basic format. In addition, Shift_JIS and UTF-16 can be specified as conversion option parameters. |
| Info: Title | <head> <title>-</title> </head> |
Get the title information from the contents of the property "Title" on the Word "Info" tab. |
| Meta-information | <head> <meta name="author" content=""> <meta name="description" content=""> <meta name="keywords" content=""> |
Converts the property items in the Word "Info" tab to name attribute values and the settings to content attribute values. the correspondence between the name attribute values and content attribute values is as follows: author: Author description: Comment keywords: Tag |
| CSS link | <link href="xxx.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" media="print"> | xxx.css is the specified CSS file name. The media attribute is optional. |
| Default style |
<head> <style>CSS style</style> </head> |
Sets the default CSS to be applied to the entire HTML. The two settings are as follows: (1) Paragraph text alignment (see Paragraph text alignment) (2) border attribute of table, vertical position of td/th (vertical-align). However, it is not output when linking external CSS. |
| JavaScript specification | <head> <script src=”xx/yy.js”></script> </head> |
xx/yy.js is the JavaScript path |
Note 1 Language judgement
Estimated from the percentage of full-width characters in a Word document and the default style language setting. Note that estimates may not be correct.
In such cases, the language can be specified in the conversion options at command line execution. See the "-lang" parameter in the table of conversion options for details.
| Conversion source | Conversion destination (HTML tag) | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body text | <body>-</body> | ||
| Title style | When outline level 1 is set for the title style. | <h1>-</h1> | Some of the title styles registered in Word's Style Gallery have outline level 1 set, while others do not. |
| When the title style does not have an outline level set. | <p>-</p> | ||
| Paragraph | <p>content</p> |
By default, lines with only line breaks are ignored. If the "-emptyP" parameter is specified in the conversion options, lines with only line breaks are output as empty <p></p>. | |
| Forced line break | <br > | ||
| Forced page break and column break | Ignored. | ||
| Section | When the <h> start tag is at the beginning or only the <h> tag with a lower rank before it, the <section> start tag is output before the <h> start tag. When there is a <h> with a higher rank before it, output the </section>. |
Create a tree structure with the <section> tag before <h>. You can specify the outline level at which <section> tags are output by specifying the ‘-section 1-6’ parameter (an integer indicating an outline of 1 to 6) in the conversion options. |
|
| Conversion source | Conversion destination (HTML tag) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Heading 1 to Heading 6 (Heading style) | <h1>-<h6> | Set the heading style outline level to the heading rank tag. |
| Heading 7 to Heading 9 (Heading style) | <p class="l7">- <p class=”l9”> |
Heading style outline levels 7 and 8 are set as class attributes of a paragraph. |
| Paragraph outline levels 1 to 6 | <h1>-<h6> | Set the paragraph outline level to the heading rank tag. |
| Paragraph outline levels 7 to 9 | <p class="l7">- <class=”l9”> |
Paragraph outline levels 7 and 8 are set as class attributes of a paragraph. |
When an outline number is added to a paragraph for which a heading style is specified, the outline number is enclosed in a <span> tag with the class attribute value “number”, and converted to the content string of the <h> tag after specifying the class attribute value number for the outline number. If there is a space between the outline number and the heading text, the space is output as a single-byte space, or if there is a tab, the tab is deleted and a single-byte space is inserted instead.
Paragraphs with Word lists are converted to HTML lists (unordered lists) (<ul>/<li>). At this time, the bullet symbols in Word paragraphs are removed.
Paragraphs that have been numbered at the beginning of a paragraph using Word's paragraph numbering feature (numbered paragraphs) are converted as follows:
The start number is specified in the start attribute when the start number is 2 or more.
By default, paragraph style names are not output.
If you specify “-pstyle” parameter as a conversion option, the name of the paragraph style is output as the value of the class attribute of the <p> or <h> tag when a paragraph style is specified in a Word paragraph. When paragraph formatting is specified without using the paragraph style feature, the value of the class attribute is not set.
Note that if the "-embedimg" parameter is specified, the image will be embedded in the HTML file.
By default, images are converted to PNG or JPEG format, and AutoShape, line shapes inserted in Word, and shape files in EMF and WMF formats are converted to SVG format for output.
If you specify the “-throughimg” parameter in the conversion option, images and shapes inserted into Word in GIF, EMF or WMF formats are saved to the illustration output folder in their original formats without file format conversion.
Saves the layout option type specified in Word format as the <img> class attribute.
| Conversion source | Options | class attribute |
|---|---|---|
| In Line with Text |  |
class="inline" |
|
With Text Wrapping 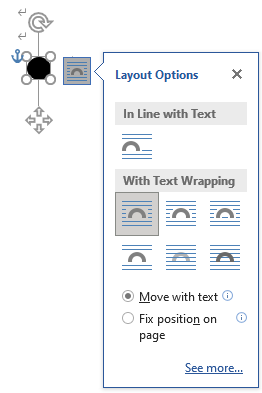
|
Common for “With Text Wrapping” | class="block" |
Square  | class="block square" | |
Tight  | class="class="block tight" | |
Through  | class="block through" | |
Top and Bottom  | class="block top-bottom" | |
Top and Bottom  | class="block behind" | |
In Front of Text  | class="block front" |
| CAUTION: | In CSS, the display property specifies whether the figure layout is inline or block. Since the default value of the display property is inline, even if you set “With Text Wrapping” in the Layout Options in Word, it may be displayed as “In Line with Text” in the browser. In such a case, specify as follows in CSS: img.block {
display: block
}
|
|---|
The output position of the <img> tag for an illustration that specifies string wrapping is after the end tag of the block that sets the anchor in headings and paragraphs. However, in bulleted items, it is just before the end tag.
Outputs the alt attribute to the <img> tag in HTML, where the value of the alt attribute is the string entered to the alternate text for the figure inserted in the Word document. If no string is set, "Please enter alt text." is output.
Formulas edited in Word's formula editor are output as SVG format files using <img> tags by default.
Depending on the conversion option parameters, you can convert to an external file in MathML format, convert to MathML format markup, or output as Office Math markup which is the Word's unique representation of Office Open XML formulas.
| Parameter | Output format |
|---|---|
| Unspecified | Output formulas to <img> tags as svg format files. |
| -math | Output formulas to <img> tags as MathML format files. |
| -xmath | Output formulas as mathML format markups. |
| -omath | Output formulas in Word's own Office Math format. |
| Conversion source | HTML element | Example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Table | <table> <tbody> <tr> <td> |
The value set in the "Table Styles" property: Name in the Word ribbon "Table Design" will be output as the class attribute of the <table> tag. Style names other than single-byte alphanumeric characters and some single-byte symbols are not output as the value of the class attribute. |
|
| Merge | Cell merge | <td colspan="n"> | “n” is the number of horizontally merged cells. |
| Row merge | <td rowspan="n"> | “n” is the number of vertically merged cells. | |
To output the table header tag (table header: thead), set either of the following in the first row of the table.
| Conversion source | HTML element | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
“Table Tools: Layout” 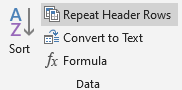
|
<thead><tr><td>...</td></tr></thead> |
The first row of the table is enclosed with <thead>. If you turn on “Repeat Header Rows”, the header rows will be repeated on each page whren the table spans pages. If you want to avoid this, turn off "Repeat Header Rows" and check "Header Row" in “Table Style Options” in “Table Design”. |
|
“Table Tools: Table Design”: “Table Style Options” 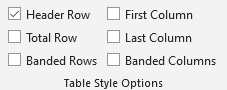
|
Select the first column of the table and check only "First Column" in "Table Style Options" in "Table Tools: Table Design" on the Word ribbon to set the cell of the first column as the header cell.
| Conversion source | HTML element | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
“Table Tools: Table Design”: “Table Style Options” 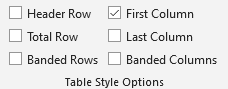
|
<tr> <th>...</th> </tr> |
The cells in the first column of the table are marked up with the header cell tags. |
When the alignment in a cell is specified in "Alignment" of the Word ribbon "Table Tools: Layout" or in the table style property cell, the class attribute is output to the <td>/<th> tag for the vertical alignment, and the style is defined in the <head> of the HTML with the <style> tag. However, if external CSS is linked or "-defstyle" is specified in the conversion option, the style definition is not output.
| Conversion source | HTML element | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Table Tools: Alignment Options in Layout 
|
Output in <head>.
<style>html{text-align:justify;}table,td,th{border:solid 1px;}td,th{vertical-align:top;}td.center,th.center{vertical-align:middle;}td.bottom,th.bottom{vertical-align:bottom;} </style> |
The relevant styles are in bold in the source code on the left. |
| Align Top | No output due to default value. | |
| Align Center (vertical) | <td class=”center”>/<th class=”center”> | |
| Align Bottom | <td class=”bottom”>/<th class=”bottom”> |
| CAUTION: |
The horizontal alignment is output as a class attribute in the paragraph <p> tag within the <td>/<th> tag. Justified: class="start" Center: class="center" Right: class="end" |
|---|
| Font group | HTML element | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Bold | strong | If the "-hstrong" parameter is specified in the conversion options, the bold set in the heading style is ignored. |
| Italic |
Ignored by default. Output with <i> tag or the following CSS style specification in the conversion options: <span style="font-style:italic;> |
|
| Underline |
Ignored by default. Optionally set the <u> tag or the following CSS style specification for output: <span style="text-decoration-line:underline> Note that the anchor text of the link is not underlined. |
|
| Strikethrough |
Ignored by default. Output with <del> tag or the following CSS style specification in the conversion options: <span style="text-decoration-line:line-through;"> |
|
| Subscript | sub | |
| Superscript | sup | |
| Text Effects and Typography | Ignored. | |
| Text Highlight Color | Ignored. | |
| Font Color |
Ignored by default. Output with the following CSS style specification in the conversion options: <span style="color;color value"> |
<span style="color:red;">text color red</span>, <span style="color:#00B050;">text color green</span> |
| Character Shading | Ignored. | |
| Enclose Characters | Ignored. | |
| Font | Ignored. | |
| Font Size | Ignored. | |
| Case | Ignored. | |
| Phonetic Guide | ruby rp rt | <ruby>紫陽花<rt>あじさい</ruby> |
| <ruby>漢<rp> (</rp><rt>かん</rt><rp>) </rp>字<rp> (</rp><rt>じ</rt><rp>) </rp></ruby> | ||
| Character Border | Ignored. |
| References | HTML element | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Link (external URL) | <a href=”Link URL”>label</a> | “Link” on the “Insert” tab on the ribbon. |
| Link (id) | <a href=”#id value”>label</a> | |
| Cross-reference | <a href=”#id value”> label</a> | References in Word documents by "Cross-references" in the "References" tab on the ribbon. |
| <span id=""> | ||
| id value | <span id=”id value”></span> | Link to bookmark "here" |
| Link target frame | <a target="target name"> |
Link target frame
<a target="target name">
Output the following choices specified in “Link” > “Target Frame” in the ribbon “Insert”, respectively, to the target name.
|
| CAUTION: |
|
|---|
Set the paragraph alignment set to the “Normal” style in the style gallery on the “Home” tab of the Microsoft Word ribbon to the <style> element of the <head>. However, when left alignment is set in the "Normal" style, text-align:start is the default value in CSS, and it is not necessary to specify the alignment, so it is not set.
Note that <style> in <head> is not output if “-defstyle” parameter is specified in the conversion option (see "Conversion options").
| Paragraph alignment | Elements and class attributes | Example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alignment of "Normal" style | Align Left | No settings. | <style></style> |
| Center | text-align:center | <style>html{text-align:center;}</style> | |
| Align Right | text-align:end | <style>html{text-align:end;}</style> | |
| Justify | text-align:justify | <style>html{text-align:justify;}</style> | |
| Distributed | text-align:justify; text-justify:auto; |
<style>html{text-align:justify;text-justify:auto;}</style> | |
If you specify the paragraph alignment other than “Normal” in the "Paragraph” group on the "Home" tab of the ribbon, the following class attributes will be set in the heading rank tag (h1 to h6) or p tag.
| Paragraph alignment | Elements and class attributes | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Align Left | class="start" | <p class=”start”>...</p> |
| Center | class="center" | <p class=”center”>...</p> |
| Align Right | class="end" | <p class=”end”>...</p> |
| Justify | class=” justify ” | <p>...</p> |
| Distributed | class="distribute" | <p class=”distribute”>...</p> |
If there are footnotes in a Word document, they are output to html.
The method of outputting footnotes depends on the following conversion options.
| Parameter | HTML element | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -footnote f(Default) |
Footnote reference marked positions in the body text: <a href="#footnote-1"> <sup>1</sup> </a> Footnote position: <aside class="footnote"> <hr> <p><span id="footnote-1"><sup>1</sup></span>Footnote is</p> </hr> </aside> Example of HTML display. 
|
Footnotes are output at the end of the text (or at the end of the text in the last HTML file if the HTML is split into separate HTML files), and the id is set so that the hyperlink given to the reference mark in the text can be used to navigate to the corresponding footnote. Footnotes are output enclosed in <aside> tags. If the “-xhtml” parameter is specified, the output is enclosed in <div> tags. If there are footnotes and endnotes, the endnotes are output after the footnotes. |
| -footnote t |
<span class="footnote" title="Footnote is"><sup>1</sup> </span> Example of HTML display.  |
You can add a <span> tag to a reference mark in the text, output the text of the corresponding footnote as the value of the “title” attribute, and display a tooltip on mouse-over of the reference mark. Note: Footnotes are not output at the end of sentences. |
| -footnote n | Footnotes and footnote reference marks are not output. |
Other options
| Parameter | Example Word settings and output results | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -endnoteId |
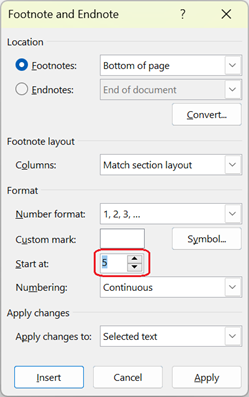 When parameters are not set: <p>This section explains footnote<a href="#footnote-1"><sup>5</sup></a>.</p> <aside class="footnote"> <hr> <p class="start"><span id="footnote-1"><sup>5</sup></span> Footnote is</p> When parameters are set: <p>This section explains footnote<a href="#footnote-5"><sup>5</sup></a>.</p> <aside class="footnote"> <hr> <p class="start"><span id="footnote-5"><sup>5</sup></span> Footnote is</p> </aside> |
When inserting a footnote in a Word document, if the start number of the sequential number of the footnote is set to a number other than “1”, the number of the footnote text (<sup> tag) in the output HTML can match the number used at the end of the “id” that specifies the footnote. |
| -customSep |
Editing Boundaries.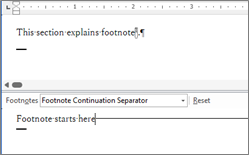 When parameters are not set: <aside class="footnote"> <hr> <p class="start"><span id="footnote-1"><sup>1</sup></span> Footnote is</p> </aside> When parameters are set: <aside class="footnote"> <p> Footnote starts here<span class="hr" style="display:inline-block;width:196.5px;height:8px;border-top:solid 1px #999"></span></p> <p class="start"><span id="footnote-1"><sup>1</sup></span> Footnote is</p> </aside> |
If footnotes are inserted, specifies the boundaries with the body text. By default, all boundaries are output as <hr> tags. If the “-customSep” parameter is specified, you can output text strings or tables edited in Word. If boundaries are included, they are output with <span> tags instead of <hr> tags. |
An anchor tag is set to an endnote symbol indicating the location of the endnote in the body text, and the id of the endnote is set to the value of the href attribute of the anchor tag.
The text of the endnote is output at the end of the document, at the same level as the paragraphs at the end of the document except for the endnote. The number of the endnote is set to id="endnote-n" (n is a number).
| Parameter | HTML element | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -footnote f(Default) |
Endnote reference marked positions in the body text: <a href="#endnote-1"><sup>i</sup></a> Endnote position: <aside class="endnote"> <hr> <p><span id="endnote-1"><sup>i</sup></span> Endnote</p> </aside> |
Endnotes are output enclosed in <aside> tags. If the “-xhtml” parameter is specified, the output is enclosed in <div> tags. If there are footnotes and endnotes, the endnotes are output after the footnotes. When anything other than “-footnote f” is specified, <aside> or <div> tags are not output. |
Other options
| Parameter | Example Word settings and output results | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -endnoteId |
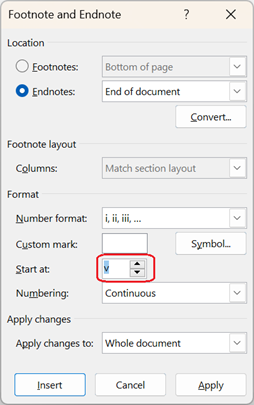 When parameters are not set: <p>This section explains endnote<a href="#endnote-1"><sup>v</sup></a>.</p> <hr> <p class="start"><span id="endnote-1"><sup>v</sup></span> Endnote is</p> When parameters are set: <p>This section explains endnote<a href="#endnote-5"><sup>v</sup></a>.</p> <hr> <p class="start"><span id="endnote-5"><sup>v</sup></span> Endnote is</p> |
When inserting a endnote in a Word document, if the start number of the sequential number of the footnote is set to a number other than “i”, the number of the endnote text (<sup> tag) in the output HTML can match the number used at the end of the “id” that specifies the endnote. |
| -customSep |
Editing Boundaries.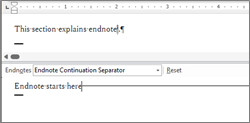 When parameters are not set: <p>This section explains endnote<a href="#endnote-1"><sup>i</sup></a>.</p> <hr> <p class="start"><span id="endnote-1"><sup>i</sup></span> Endnote is</p> When parameters are set: <p>This section explains endnote<a href="#endnote-1"><sup>i</sup></a>.</p> <p>Endnote starts here<span class="hr" style="display:inline-block;width:196.5px;height:8px;border-top:solid 1px #999"></span></p> <p class="start"><span id="endnote-1"><sup>i</sup></span> Endnote is</p> |
If endnotes are inserted, specifies the boundaries with the body text. By default, all boundaries are output as <hr> tags. If the “-customSep” parameter is specified, you can output text strings or tables edited in Word. If boundaries are included, they are output with <span> tags instead of <hr> tags. |
The table of contents section created using Word's table of contents function is output to an HTML file with a link to the heading section in the table of contents item. The table of contents is output as follows:
| CAUTION: |
|
|---|
| HTML element | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| ① | <a id="mobile-side-btn" href="javascript:;"><span class="mobile-side-btn-icon" id="mobile-side-btn-icon"></span></a> |
<a></a> immediately before the <nav> tag can be used as buttons to control the display of the table of contents when displayed on mobile devices. Please refer to the following web page for a sample of the buttons for mobile devices. https://www.antennahouse.com/html-on-word-samples |
| ② | <nav class="toc-wrap"> |
The table of contents sections ④ and ⑤ are enclosed in ② <nav> and ③ <div> tags and output. If the "-split" + "-tocout" parameters are specified in the conversion options, ③ to ⑤ are output as separate HTML file "inc-toc.html". |
| ③ | <div id="toc"> | |
| ④ | <p class="toc-heading">[Table of contents heading]</p> |
The paragraph style name (blanks are converted to "-") set for the paragraph of the table of contents heading will be output. For a table of contents inserted using Word's "Built-In" table of contents function, <p class=”toc-heading”> will be output by default. |
| ⑤ | <p class="toc-[n]"><a href="[ Link to the corresponding heading id]">[Heading name]</p> |
The paragraph style name (blanks are replaced with “-“) set for the paragraph of each item in the table of contents will be output. For a table of contents inserted using Word’s “Built-In” table of contents function, <p class=”toc-[n]”> will be output by default. ([n] is a number from 1 to 6.) The link to the corresponding heading id will output a URL starting with "#_Toc". If the HTML file is split and output by specifying the "-split 1|2|3" parameter in the conversion options, the output will be the file name and id of the HTML file to be split. (e.g. index-1.html#_TocXXX) |
| Specified parameter | Output | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Only -split 1|2|3 |
The table ① to ⑤ in Section "Table of contents output" is output immediately after the <body> tag in all HTML files to be split into separate output files. At this time, "active" is output as the class attribute of the paragraph <p> tag of the table of contents item (the highest hierarchical level in the page) that indicates the own HTML file. |
|
| -split 1|2|3 -tocout |
Output table ③ to ⑤ from the table in "Table of contents output" as separate HTML files (inc-toc.html). In addition, ① and ② are output immediately after the <body> tag in all HTML files to be output separately. |
inc-toc.html can be used to load into a split-output HTML file using JavaScript or to load into other HTML files. For this reason, inc-toc.html does not output tags other than ③ to ⑤ such as <html><head><body>, etc.. Please refer to the following web page for an example of loading a table of contents section using JavaScript. https://www.antennahouse.com/html-on-word-samples |
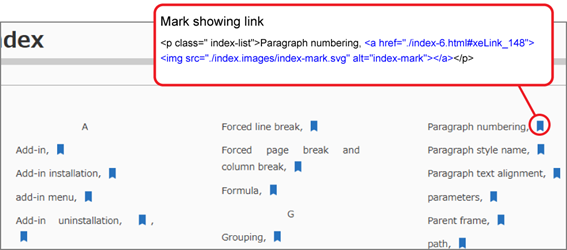
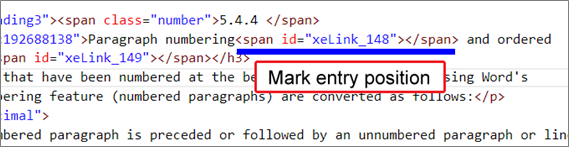
*Index hyperlinks are output as default. Parameters do not need to be specified.
*Only indexes registered with “Mark Entry” in the “Reference” of the Word ribbon are supported.
*If XE (Index Entry) fields registered in Mark Entry are changed manually, or XE and INDEX fields are inserted using the field function, they may not be output as displayed in Word or may not be output correctly.
*The settings made in the "Options" and "Page number format" items of the "Mark Entry" screen will not be reflected in the output HTML index. (Page numbers will not be output.)
When the "-split 1|2|3" parameter is specified in the conversion options, the HTML file will be split and output according to the outline level of the paragraphs specified in the Word document. The outline levels that can be specified are 1 to 3.
The contents of the splitting are as follows:
| Item | Content | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Splitting point | Within the outline level of a paragraph in Word (the value following the specified -split), split just before the next paragraph of the same level. | If the value is specified as 2 or 3, they are also divided immediately before the higher level, respectively. |
| Output file name | The split output file names are output as sequential numbers connected by "-" (hyphen) before the specified file name extension (.html). The first page is the specified output file name. |
Example of specifying index.html as the output file name. index.html, index-1.html, index-2.html, index-3.html, ... |
| Output HTML |
<html>, <meta>, <style>, <link> (CSS), <script> (JavaScritpt) and <body> tags are common to all pages. The <title> tag is set to [outline level 1 label] - [outline level 2 label] - [outline level 3 label] - [title set in the Word document information] for the relevant page. |
Labels below the specified outline level will not be output within the <title> tag. e.g. -split 1 is specified [outline level 1 label] - [title set in Word document information]. |
| Table of contents | The table of contents is output at the top of all split HTML files (immediately after the <body> tag). | If the "-tocout" parameter is specified at the same time, <div id="toc"></div> in the table of contents is output as a separate HTML file (inc-toc.html). For details, please refer to "Table of contents for split output". |
| Page link | If the "-pagenavi" parameter is specified when the "-split 1|2|3" parameter is specified in the conversion options, links are output that go to the previous and next pages of the HTML file being displayed. | See "Page link output" for details. |
When the "-split 1|2|3" parameter is specified in the conversion options and the "-pagenavi" parameter is specified, links are output at the top (immediately after the table of contents, if any) and bottom (immediately before the </body> tag) of the split HTML file, based on the sequential number of the HTML file name to be output.
The link labels can be output in Japanese or English by specifying the value following the parameter:
| Value | Link label | Note |
|---|---|---|
| ja | "前へ" and "次へ" in Japanese. | If there is no previous or next page, "前へ" or "次へ" links are not output. |
| If you specify anything other than "ja" or omit it. | “Prev” and “Next” in English. | If there is no previous or next page, "Prev" or "Next" links are not output. |
<nav> <div class="pagenavi-wrap-top"> <div class="pagenavi-prev"> <a href="index.html">Prev</a></div> <div class="pagenavi-next"> <a href="index-2.html">Next</a></div> </div> </nav>
<nav> <div class="pagenavi-wrap-bottom"> <div class="pagenavi-prev"> <a href="index.html">Prev</a></div> <div class="pagenavi-next"> <a href="index-2.html">Next</a></div> </div></nav>